Nursing is not about giving medications and taking care of patients only. It is also about thinking critically to provide holistic care to patients for a better outcome. For that, nurses are required to create nursing care plans.
Writing a nursing care plan (NCP) is one of the most crucial as well as challenging tasks for nursing students. The reason is its lack of understanding. Many nursing students are often unaware of the correct structure and approach to these nursing plans. Due to this, they are unable to benefit from them. This also results in poor patient care. “In the current study, about 83% of respondents said that lack of preparedness or knowledge about the nursing process or some of its parts affects the implementation of the nursing process.”(source: National Institutes of Health)
These nursing care plans act as the backbone for nurses. It helps them to have a better judgement of the patient’s condition, enabling them to provide holistic treatment for better outcomes. If you want to create a high-quality and effective nursing care plan, you must first understand what is a care plan in nursing, and how you can make a top-quality one.
So, are you ready to level up your nursing care plans? I will share everything you need to know about these nursing care plans. Also, you can access free templates. Let’s dive into it!
What is a Nursing Care Plan?
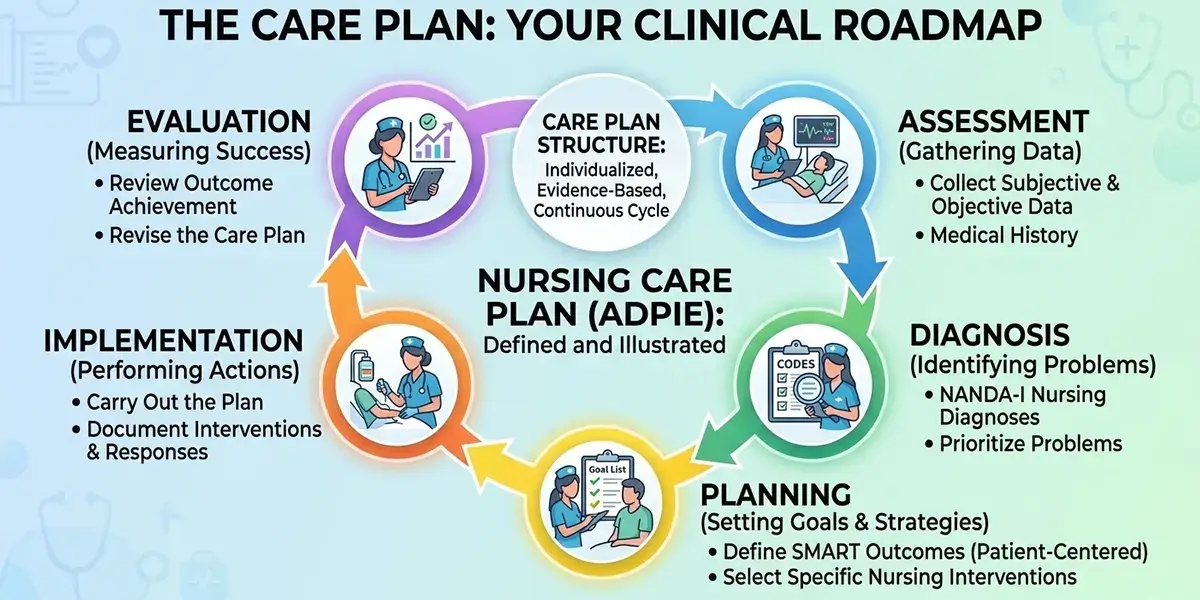
Before learning how to write a nursing care plan, you must first understand what a care plan in nursing is.
Definition of Nursing Care Plan:
A Nursing Care Plan (NCP) is a structured document that allows nurses to outline a patient’s specific health needs. It enables professionals to compile and share crucial information related to patients’ diagnosis and treatment process. It has four common types, including:
- Standardised care plan
- Individualised care plan
- Student care plan
- AI-assisted care plan
These nursing care plans serve as a roadmap for nurses, allowing them to stay updated with the next steps in a patient’s care. It also plays an essential role in providing holistic care to patients. Many students often fail to differentiate between a healthcare assistant vs nurse, and often get confused whether a nursing care plan is written by a healthcare assistant or by a nurse. It is written by a nurse.
What is the Difference Between Nursing Diagnosis and Medical Diagnosis?
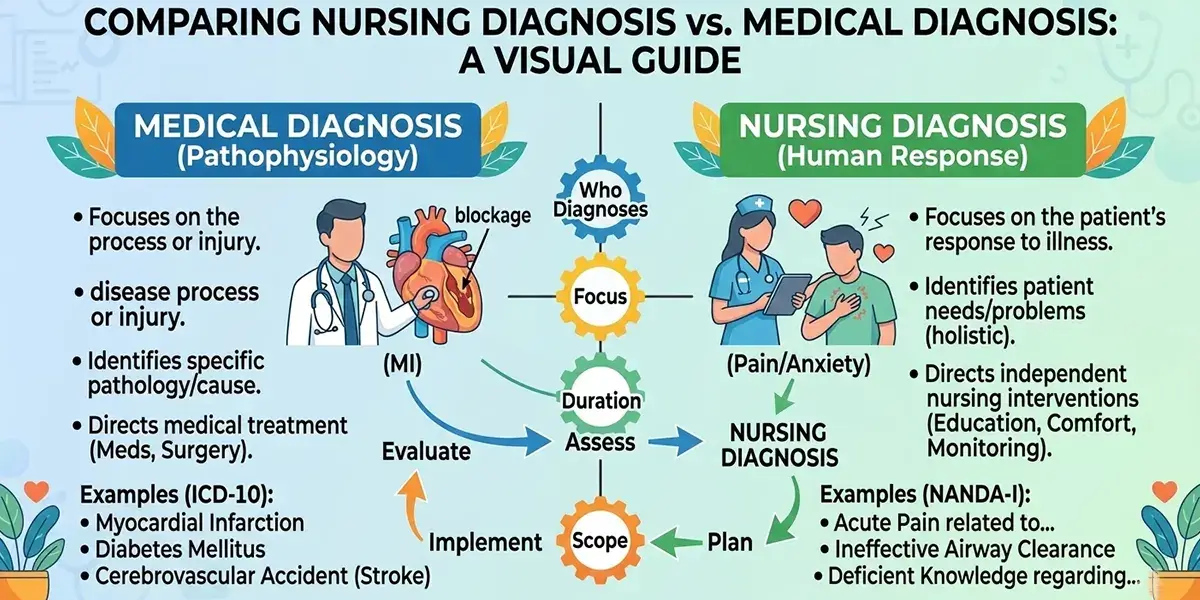
Many nursing students often fail to distinguish between nursing and medical diagnoses. Here is how you can differentiate between them:
Focus:
To begin with, the main focus of medical diagnosis is to identify an illness or disease. Besides, the main focus of nursing diagnosis is to identify the patient’s physical, psychological, social, and spiritual response to that illness or disease.
Goal:
The goal of nursing diagnosis is to understand the patient’s response and improve the holistic care. And the goal of medical diagnosis is to treat the patient and cure the disease.
Duration:
Medical diagnosis doesn’t really change until and unless the disease is cured. But nursing diagnoses frequently change as the patient’s health changes.
You can also use this table to have a better understanding:
| Nursing Diagnosis | Medical Diagnosis |
|---|---|
| Its main focus is to identify patients’ responses to specific illnesses or diseases. | Its main focus is to identify a specific illness or disease. |
| The goal is to provide effective, holistic care. | The goal is to treat and cure the disease. |
| Nursing diagnoses change frequently. | Medical diagnoses rarely change until the disease is cured. |
| Eg: Ineffective airway clearance | Eg: Pneumonia |
What are the Different Types of Nursing Care Plans?
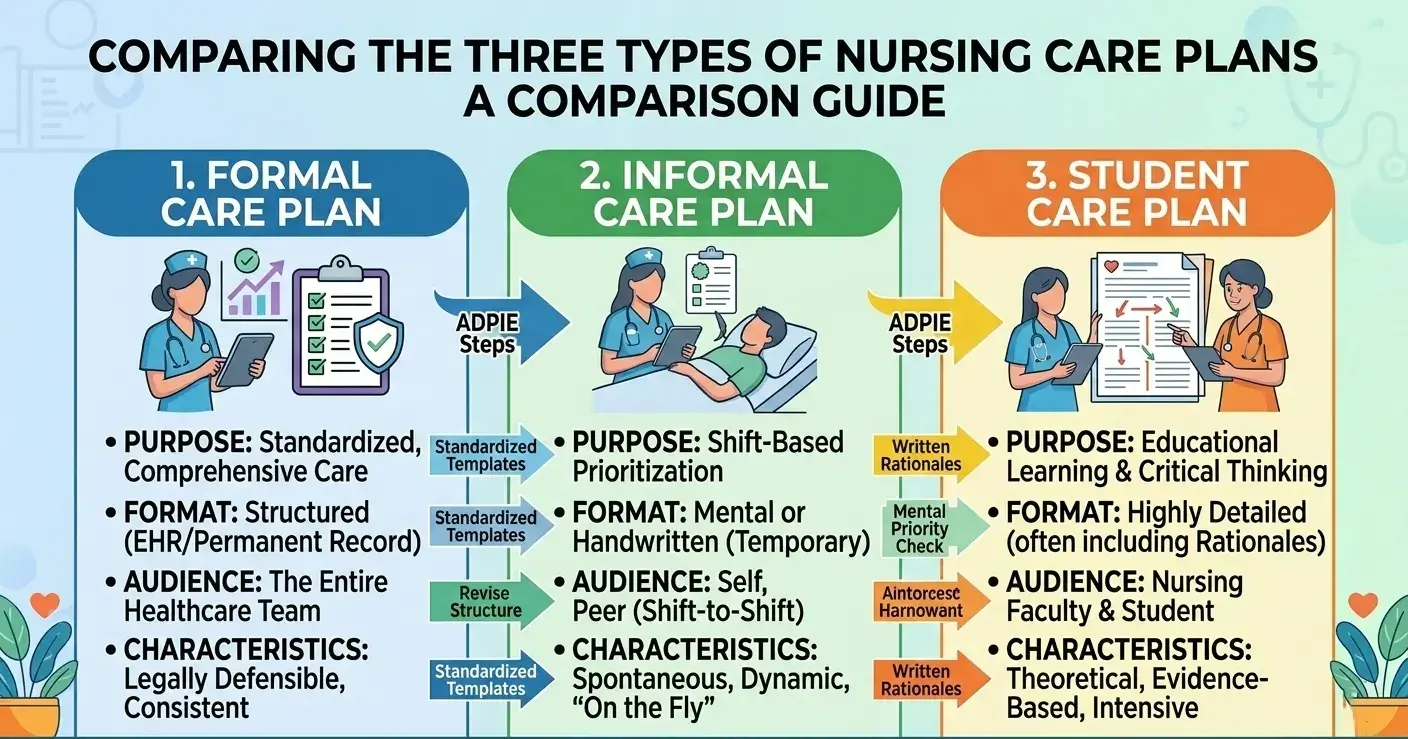
The nursing care plans (NCPs) are of three different types, which include:
- Formal care plan:
- Informal care plan:
- Student care plan:
To ensure that you create a top-notch and effective care plan for nursing, you must first have a strong understanding of its types.
Informal Care Plans:
The very first type of NCP is informal care plans, which is one of the most common types. Nurses make care plans in their minds. Nurses often use these care plans when they are required to make quick decisions, mostly in emergency cases. But these informal care plans are not considered fully reliable. The reason is that they lack legal documentation, due to which other nursing staff cannot check it. This leads to issues with continuity of care. Moreover, these care plans are made without any track of the patient’s history. This can raise concerns about patients’ safety.
Formal Care Plans:
The formal care plans are quite different from the informal care plans. These are properly structured (written or computerised) documents that help nurses identify the health needs of a patient. This helps them provide personalised care to patients, using evidence-based practice. Also, it helps nurses to avoid complications in patient care. The formal care plans are further divided into two types:
Standardise Care Plans:
These are ready-to-use care plans for patients with common and predictable health conditions, such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, heart failure, and others.
Individualised Care Plans:
The individualised care plans are customised according to a patient’s specific needs and health condition. The diseases include stroke, dementia/alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s disease, eating disorders, and many more.
Student Care Plans:
Student care plans are detailed plans that help nurses to develop strong critical thinking, assessment, and care planning skills. As compared to practical nurses, students are required to make comprehensive care plans, as they work as a learning tool for them. Many nursing programs include assignments of these nursing care plans, allowing students to remain familiar with their format and importance.
List of Nursing Care Plans
One of the most commonly asked questions among nursing students is, in which clinical conditions can we use nursing care plans? The answer is simple. You can create an effective nursing care plan for various clinical conditions, examples include:
- Nursing care plan for pain
- Nursing care plan for Parkinson’s disease
- Diabetes nursing care plan/nursing care plan diabetes mellitus
- Nursing care plan for Dementia/Alzheimer’s nursing care plan
- Nursing diagnosis and care plan for hypertension
- Neurological nursing care plan
- Nursing care plan for the elderly
- Multiple sclerosis nursing care plan
- Nursing wound care plan
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease nursing care plan/nursing care plan for COPD
- Nursing care plan for mobility
- Nursing care plan for skin integrity
Why are Nursing Care Plans Important?
One of the main reasons why nursing students ignore the implementation of these nursing care plans in their practical learning is unfamiliarity with their importance. The following are the key reasons why nursing care plans are important:
Improved Patient Outcomes:
Firstly, one of the key importance of nursing care plans is that they improve patient outcomes. Nurses use these plans to understand patients’ health conditions properly. This means that they are able to provide better care to patients, eventually leading to improved patient outcomes. Even if the patient lives in a rural or underserved area, nurses can create a structured care plan to provide proper care through telehealth nursing.
Acts as a Roadmap for Nurses:
Secondly, these care plans are really crucial for nurses as they act as a roadmap for a patient’s care. When nurses include critical information about patients’ health conditions, they are able to make informed decisions for better care. Besides, it also helps nurses to set SMART (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-bound) goals. This way, you can track patients’ progress efficiently.
Continuity of Care:
Further, most of the time, nurses get their shifts changed. Due to this, they have to take care of other patients. Using a well-structured nursing care plan can help nurses provide continuous care to patients, ensuring every healthcare professional follows the same plan despite the changes of shifts. This means that the patient receives the same treatment as before, no matter whether the previous nurse is present or not.
Offers Holistic Patient Care:
Nursing care plans are also pretty helpful for nurses, enabling them to identify health issues of each individual. This allows them to offer holistic care to patients, which results in better patient recovery.
Ensures Patients’ Safety:
Also, different patients often have allergies or complications with different things. Making a proper care plan allows nurses to identify and prevent these complications for a better patient outcome. It also ensures that the patient is receiving high-quality and reliable care.
What are the Key Components of a Nursing Care Plan?
Many students are also unaware of the key components of nursing care plans. Due to this, they are unable to make high-quality nursing care plans. To avoid this, you must be familiar with its key components.
Assessment:
The very first component is assessment. For assessment, nurses are required to use their critical thinking skills and collect data. You need to collect subjective and objective data from patients. The subjective data includes verbal statements, whereas the objective data includes weight, height, and other factors. The assessment data often includes:
- Symptoms of the patient
- Lab reports
- Physical findings
- Vital signs
- Mental health condition
- Medical history
When you are assessing, you must ensure to avoid any errors, as even small mistakes can result in ineffective nursing care plans. This also leads to poor patient outcomes.
Nursing Diagnosis:
Nursing diagnoses are quite different from medical diagnoses. Nurses are required to identify patients’ needs and responses to their illness. For a perfect diagnosis, you must properly analyse the assessment data and identify the actual or potential health issues and risks. Many nurses, even in the United Kingdom, use the NANDA-International (NANDA-I) nursing diagnosis for better identification. For a top-notch diagnosis, you can use these three steps:
- Problem
- Related to (causes)
- As evidenced by (signs and symptoms)
Planning (Expected Outcomes):
After diagnosis, nurses must collaborate with patients and their families in order to set SMART goals. The goals must be:
- Smart
- Measurable
- Attainable
- Relevant
- Time-bound
Also, your goals can be either long-term or short-term or both. When you are setting the goal, you must ensure that you have considered the diagnosis, overall condition, and other relevant information about the patient. This will help you create goals that are not only realistic but also achievable.
Nursing Interventions:
Once you have set the goals, it is time to take specific action and address the patients’ needs through diagnosis. But before moving on, you must understand what nursing intervention actually means. In simpler words, nursing interventions are actions taken by nurses that are specific and evidence-based. These actions help nurses prevent complications in patient care and promote better patient outcomes. The nursing interventions are of three types, including:
Independent:
The very first type is independent intervention. In such interventions, nurses initiate the action independently, such as providing education to the patient or offering comfort measures.
Dependent:
Besides, in dependent interventions, nurses follow the orders from physicians or healthcare professionals.
Collaborative:
In this type of intervention, nurses are required to collaborate with other healthcare team members, including dietitians or therapists.
Rationales:
Nursing rationales are also an important component of nursing care plans. These are scientific and evidence-based justifications for nursing interventions. In other words, they explain why a specific action is necessary for improving patient outcomes. In the nursing profession, these rationales are often not included in the nursing care plans. However, they are pretty important for nursing students, as they help them have a deep understanding of interventions. It also has three types, including:
- Physiological
- Psychological
- Educational
Evaluation:
Lastly, you need to evaluate the patient’s progress and check whether they met your expected outcomes or not. This will help you determine whether your interventions are effective or need some changes. You can also use the six-stage framework of the Gibbs Reflective Cycle to ensure that your plan is effective. Moreover, it also helps you assess both negative and positive aspects of your care plan. Also, you can identify what you did well and what still needs improvement for the future.
How to Write a Nursing Care Plan?
Now comes the main part, writing a nursing care plan.
Writing nursing care plans is indeed difficult, but with the right approach, you will be able to create a high-quality care plan. To write a top-notch nursing care plan, follow these steps:
Step 1: Data Collection
The very first step in writing a nursing care plan is data collection. This step helps you build the foundation of your entire plan. If your data is incomplete or inaccurate, the rest of your care plan will also be weak.
You can collect data in two main ways: subjective and objective. Subjective data includes what the patient tells you, like their pain level, dizziness, nausea, or emotional concerns. Objective data includes what you observe and measure, such as vital signs, lab results, physical assessment findings, and diagnostic reports.
You can collect the data through:
- Patient interviews
- Physical examination
- Reviewing medical records
- Lab and imaging reports
- Discussions with patients’ family members
You must always ensure that your documentation is clear and precise, as even minor errors at this stage can impact patient outcomes.
Step 2: Data Analysis
After gathering information, the next step is to analyse the data. But what does that mean? This means carefully reviewing all the details you have collected and identifying their patterns. You should also compare abnormal findings with normal ranges and look for connections between symptoms and physical signs.
Clustering related data is also very helpful for nurses, such as shortness of breath, low oxygen saturation, and abnormal lung sounds, which indicate a respiratory issue. You are required to use your critical thinking skills in this step. Therefore, you must logically connect the evidence before deciding on a nursing diagnosis instead of jumping to conclusions.
Step 3: Set Your Priorities
Besides that, not all patient problems need immediate attention. That is why prioritisation is essential. As a nurse, you need to decide which issue requires urgent care. For that, you can use the ABC rule, which stands for Airway, Breathing, and Circulation. Life-threatening problems always come first. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is also useful in identifying basic physiological needs before psychological concerns. Also, prioritising ensures patient safety and makes your care plan realistic and more manageable.
Step 4: Establish Goals and Expected Outcomes
Once your priorities are clear, you must set SMART goals. These goals are really crucial, as they give direction to your interventions. Also, ensure that your goals follow the SMART framework, which means they must be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound. Instead of writing “Patient will improve,” you must write “Patient’s blood pressure will remain within normal range within 48 hours.” Setting clear goals makes evaluation easier later. Besides, you must also involve the patient in goal-setting, as it also increases motivation and cooperation.
Step 5: Select Nursing Interventions
After setting goals, you have to choose appropriate nursing interventions. Make sure that these actions directly address the identified nursing diagnosis. Your chosen interventions can be independent, dependent, or collaborative. Always ensure interventions are evidence-based and specific, and also avoid writing vague statements.
Step 6: Providing Rationale
Further, each intervention should include a clear rationale. A rationale explains why you are performing a particular action. It strengthens your care plan and shows your understanding of scientific principles. These rationales are quite important for nursing students because they demonstrate critical thinking skills and theoretical knowledge.
Step 7: Evaluation
Lastly, evaluation is the final step of the nursing care plan writing process. It helps you to determine whether your goals were achieved or not. After implementing interventions, you are required to reassess the patient’s condition. If the patient meets your expected outcomes, you can surely continue the plan. However, if they don’t meet the expected outcomes, you need to modify the plan.
Besides, to create a better nursing care plan, nursing students must also have a strong grasp on the Driscoll Model of Reflection. Even if you are a novice, having a better understanding of this reflective model will help you enhance the quality of your care plans.
Struggling to write your nursing care plan? Seek professional help!
Do you find writing nursing care plans difficult? But now you don’t have to worry because Nursing Assignment Helpers is here for you. Get 100% plagiarism-free Nursing Care Plan Writing Help, along with round-the-clock assistance from our experts.

Formats of Nursing Care Plans
Different institutions require different formats of nursing care plans. But the structure and goals remain the same. The following are the most common formats of nursing care plans that are used worldwide:
3-Column Format:
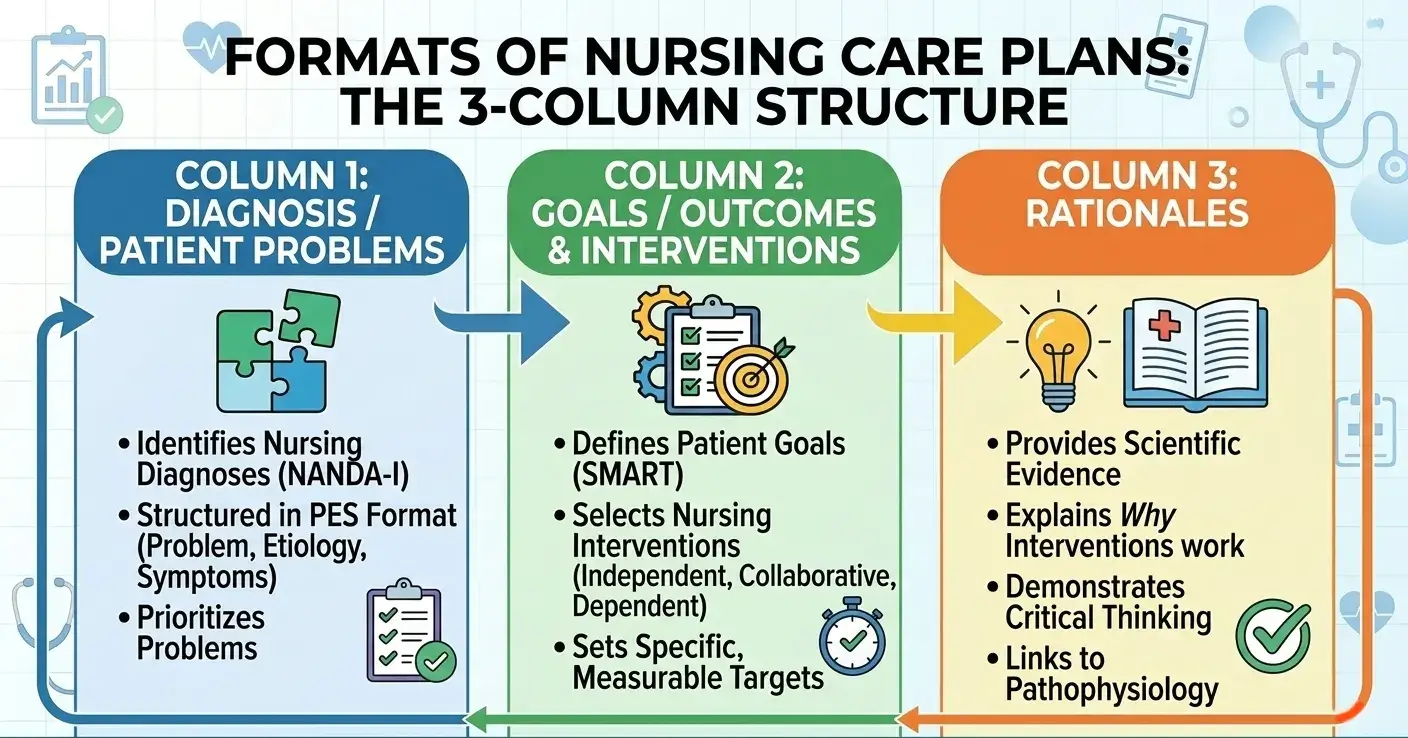
The 3-column format is one of the simplest formats. It usually includes:
- Nursing Diagnosis
- Goals/Expected Outcomes
- Nursing Interventions
This format is pretty easy and time-saving, and is commonly used in busy clinical settings where quick documentation is needed.
4-Column Format:
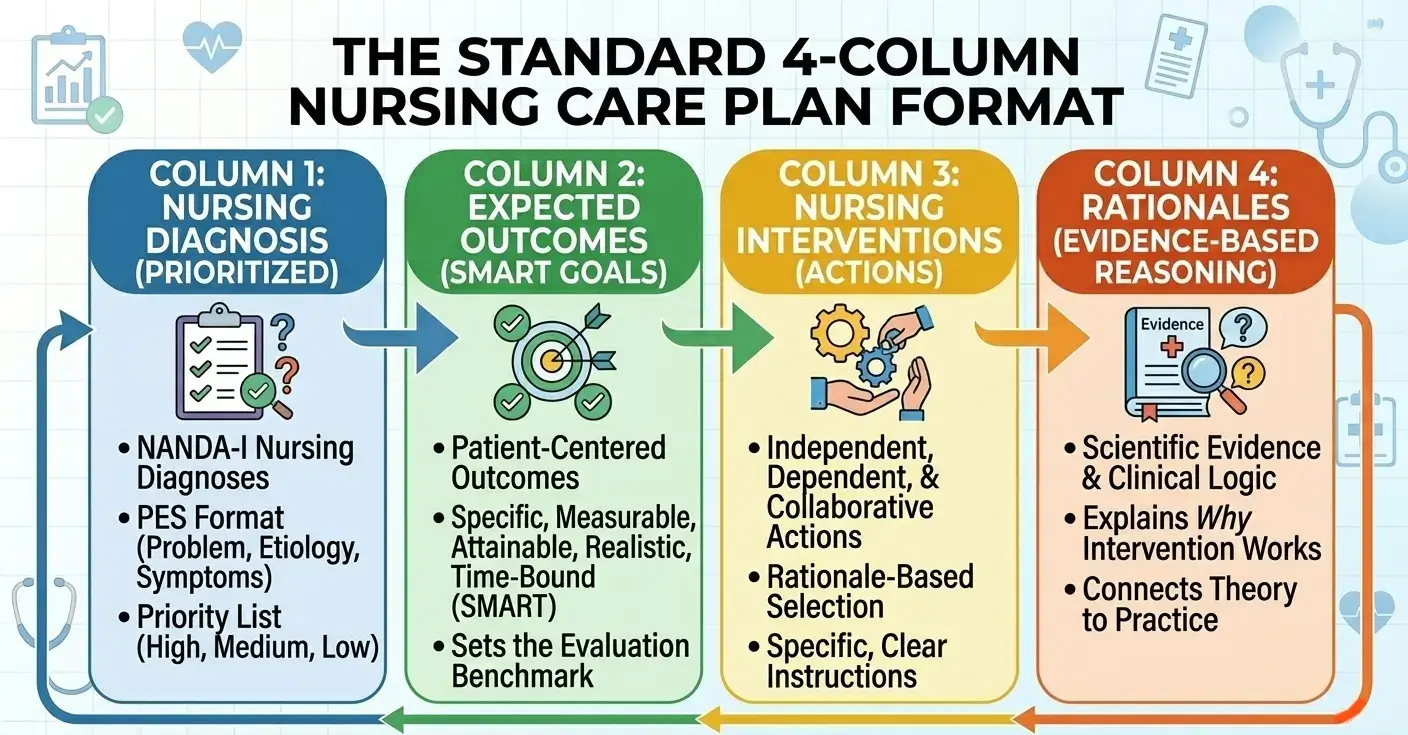
Besides the 3-column format, the 4-column format is also pretty common among nurses. It includes:
- Assessment
- Nursing Diagnosis
- Goals
- Interventions
This format provides more detail than the 3-column structure. It also connects assessment data with diagnosis and actions more clearly.
5-Column Format:
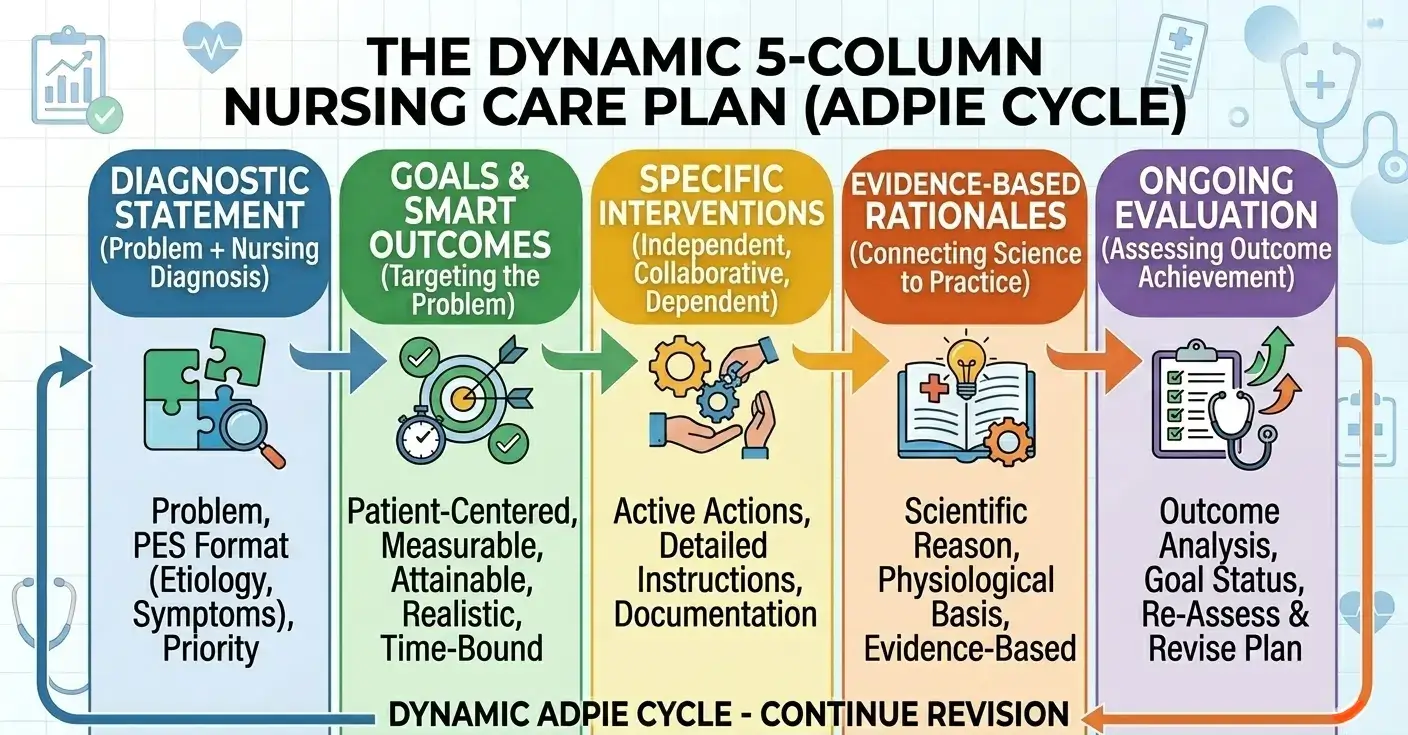
For a more comprehensive care plan, you can use the 5-column format, as it allows you to get better details. It includes:
- Assessment
- Nursing Diagnosis
- Goals/Outcomes
- Interventions
- Evaluation
This format is widely used by nursing students because it covers the full nursing process. It also helps in systematic learning and clear presentation.
Sample of Nursing Care Plan
Are you still confused about the structure and format of a professional and well-structured nursing care plan? If this is the case, then you must not worry. I have provided a sample of nursing care plan for you. You can download the Nursing Care Plan Template PDF for free.
Real-Life Example
To have a better understanding of how you must create a nursing care plan, you must take a look at this example:
Assessment:
Patient reports sharp abdominal pain rated 8/10. Blood pressure is slightly elevated.
Nursing Diagnosis:
Acute pain related to inflammation, as evidenced by the patient’s verbal report of an 8/10 pain score and guarding behaviour.
Goal:
Patient will report pain level reduced to 3/10 or less within 24 hours.
Interventions:
- Assess pain level every 4 hours.
- Administer prescribed analgesics.
- Encourage relaxation techniques.
- Position the patient comfortably.
Evaluation:
After 24 hours, the patient reports pain reduced to 3/10. Goal achieved.
Common Challenges in Nursing Care Planning
Writing a nursing care plan may look simple in theory, but nursing students and practising nurses often find it pretty challenging. If you want to do well in nursing, you must overcome these challenges efficiently. The following are some challenges that nurses often face in nursing care planning:
1. Lack of Understanding of Nursing Diagnoses
Firstly, one of the biggest challenges is that nursing students often get confused about nursing diagnoses. Many students are unable to distinguish between medical diagnoses and nursing diagnoses. Like writing “Diabetes Mellitus” instead of identifying “Imbalanced nutrition” or “Risk for unstable blood glucose level.”
Some other common issues that nursing students face include:
- Using incorrect NANDA terminology
- Writing vague problem statements
- Failing to link diagnosis with assessment data
- Not identifying “related to” and “as evidenced by” properly
Remember, your entire care plan becomes weak and ineffective without a clear diagnosis.
2. Limited Clinical Exposure
In addition, students who have limited hospital experience often struggle with creating an effective care plan. They often feel unsure about selecting appropriate interventions or setting realistic goals.
This lack of exposure can lead to:
- Overly theoretical care plans
- Interventions that are not practical
- Fear of making mistakes
- Low confidence in decision-making
Clinical experience improves critical thinking. The more exposure you gain, the better your care plans become.
3. Time Constraints in Clinical Settings
Besides, nursing students have to manage multiple patients during a shift. In addition, they have to balance their studies concurrently. Writing a detailed care plan in such settings can feel quite overwhelming.
Time pressure may result in:
- Incomplete documentation
- Skipping evaluation
- Copying generic templates
- Rushing through the assessment
However, proper time management and practice can make the process smoother for you.
4. Poor Critical Thinking Skills
Having strong critical thinking skills is also essential for nursing students if they want to create a practical and effective nursing care plan. Some students consider these care plans as just assignments. Because of this, they fail to understand the patients’ needs and just focus on completing the task. They also lack proper critical thinking skills, due to which they are unable to make a logical care plan.
Signs of weak critical thinking include:
- Writing identical care plans for different patients
- Ignoring patient-specific factors
- Failing to update the plan when conditions change
- Choosing interventions without scientific reasoning
To become a nurse who is perfect in their duties, you must first improve your critical thinking skills. For that, you must practice and seek feedback from your instructors and senior nurses.
Tips for Effective Nursing Plans
Many nursing students fail to create a good-quality nursing care plan. The reason? Not following practical strategies. Creating an effective nursing care plan becomes easier when you follow practical strategies. The following are some effective tips that can help you enhance the quality of your nursing care plan.
1. Start with a Thorough Assessment:
As I have discussed earlier, assessment is the foundation of your care plan. You won’t be able to diagnose correctly if your assessment is incomplete. Hence, you must begin with a thorough assessment. For a correct assessment, you must ensure to:
- Collect both subjective and objective data
- Review lab reports carefully
- Observe patient behaviour and physical signs
- Ask open-ended questions to gather detailed information
Always remember that if your data is accurate, you will also have an accurate diagnosis.
2. Use Approved Nursing Diagnosis Guidelines:
In addition, you must always rely on approved nursing diagnosis guidelines. This will help you ensure professionalism and clarity in your care plan. For that, you should:
- Follow the proper diagnostic structure
- Avoid using medical diagnoses in place of nursing diagnoses
- Support your diagnosis with evidence from assessment data
This will surely help you to make your nursing care plan not only systematic but also highly credible.
3. Prioritise Patient-Centred Care:
Another important thing that you need to understand is that every patient is different. This is why you must avoid copying care plans without any modification. Instead, you must:
- Consider the patient’s age, culture, and background
- Involve the patient in goal setting
- Respect their preferences and values
Providing holistic care to patients enables nurses to improve patient outcomes, leading to faster and better recovery. Besides that, you must also improve cultural competence in nursing to create a safe and comfortable environment for patients.
4. Keep Goals Realistic and Measurable:
Besides, it is very important for you to keep your goals realistic and measurable. And how can you do that? By using the SMART (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time-bound) framework. Remember these things when you are writing your goals:
- Use specific numbers where possible
- Set clear time frames
- Ensure the goal is achievable based on the patient’s condition
You can set your goal as “Patient will maintain oxygen saturation above 95% within 8 hours.” This will make evaluation a lot easier and more effective for you.
5. Support Interventions with Rationales
Also, you must add rationales to support your interventions. This will also strengthen your understanding.
Ask yourself:
- Why am I performing this intervention?
- How will this improve patient outcomes?
- Is this action evidence-based?
Writing clear rationales will help you show your logical thinking and enhance your professional growth.
6. Review and Update the Care Plan Regularly
A nursing care plan is not a one-time document. It must change as the patient’s condition changes. This is why you must update your care plan regularly. You need to:
- Reassess patient status
- Modify goals if necessary
- Add new diagnoses if new problems arise
- Remove resolved issues
Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Nursing Care Plan
Even professional nurses with years of experience can make common errors while writing nursing care plans. To ensure that you create high-quality and error-free care plans, you must avoid the following mistakes:
1. Writing Vague or General Statements
The very first and most common mistake that most nursing students often repeat is that they write statements that are too vague or too general. Your care plan must be clear and specific. You must avoid writing statements like “Patient will feel better” or “Monitor patient.”
Instead, you must:
- Specify what you will monitor
- Include measurable outcomes
- Define a clear time frame
2. Confusing Nursing and Medical Diagnoses
Besides, another very common mistake is confusing nursing diagnoses with medical diagnoses. Writing “Diabetes Mellitus” as a nursing diagnosis is incorrect. That is a medical diagnosis.
A correct nursing diagnosis would focus on the patient’s response, such as:
- Imbalanced nutrition
- Risk for unstable blood glucose level
- Impaired skin integrity
You must always have a strong focus on the patient’s reaction to the illness rather than the disease itself.
3. Setting Unrealistic Goals
Also, you must not set goals that are unrealistic or unachievable within the desired time. Instead, your goals should be achievable. Writing “Patient will completely recover in 24 hours” is surely not realistic for chronic conditions.
However, if you set unrealistic goals, they can:
- Lead to poor evaluation results
- Cause frustration
- Reduce the credibility of your plan
That is why you must ensure that your goals are practical and patient-centred.
4. Ignoring Patient Involvement
Another mistake that you must avoid is excluding the patient from the planning process. Remember that nursing care is always patient-centred, and failing to involve patients may result in:
- Lack of cooperation
- Poor adherence to treatment
- Reduced motivation
Therefore, you must always discuss goals and interventions with the patient whenever possible.
5. Skipping Evaluation
Some students complete assessments and interventions, but often forget evaluation. And without evaluation, their care plan remains incomplete. The evaluation not only allows you to measure the effectiveness of your plan and identify necessary changes, but it also helps you improve your plan for a better future.
All in All!
In a nutshell, a well-written and properly structured nursing care plan is crucial in nursing. It not only acts as a roadmap for nurses but also improves patient outcomes. However, you must remember that a nursing diagnosis is different from a medical diagnosis. Differentiating between them is actually essential for creating top-notch nursing care plans. Besides, you must ensure that your care plan includes these six crucial components:
- Assessment
- Nursing diagnosis
- Planning
- Nursing interventions
- Rationales
- Evaluation
Writing these nursing care plans is often mandatory for nursing students as part of their assignments. Similarly, nurses must also create them to provide holistic care to the patient for better recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
What is a nursing care plan?
A nursing care plan (NCP) is a guide that helps nurses identify patients’ needs and responses to specific health conditions. These care plans help them provide better and holistic care to patients, resulting in improved patient outcomes.
What are the care plans in nursing?
The care plans in nursing are documents that focus on the patient’s specific needs and goals. Nurses use these plans to implement evidence-based actions to address these needs and goals.
How to write a nursing care plan?
To write a nursing care plan, you must follow these steps:
- Step 1: Data Collection
- Step 2: Data Analysis
- Step 3: Set Your Priorities
- Step 4: Establish Goals and Expected Outcomes
- Step 5: Select Nursing Interventions
- Step 6: Providing Rationale
- Step 7: Evaluation
What is the difference between a nursing diagnosis and a medical diagnosis?
The difference is that a medical diagnosis identifies a specific illness or disease, whereas a nursing diagnosis identifies the response of the patient to the illness or disease.
What are the main components of a nursing care plan?
The following are the main components of a nursing care plan:
- Assessment
- Nursing diagnosis
- Planning and expected outcomes
- Nursing interventions
- Rationales
- Evaluation
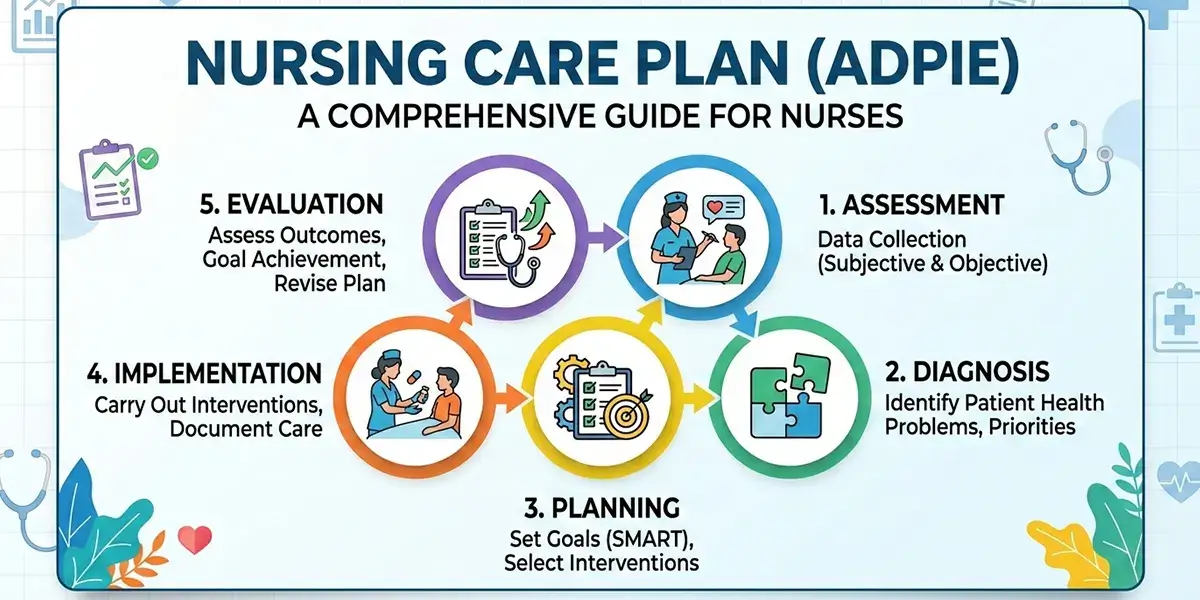
What is ADPIE?
The ADPIE is an acronym for the nursing process, which stands for:
- Assessment
- Diagnosis
- Planning
- Implementation
- Evaluation
Why are nursing care plans important?
Nursing plans are important for the following reasons:
- Ensures continuity of care
- Improves patient outcomes
- Acts as a roadmap for nurses
- Offers patient-centred care
- Prioritises patients’ safety
What is the main purpose of a nursing care plan?
The main purpose of a nursing care plan is to provide a well-structured and evidence-based document that acts as a roadmap for nurses, allowing them to offer holistic, safe, and consistent care.
What are the SMART goals in nursing care planning?
The SMART goals in nursing care planning are:
- Specific
- Measurable
- Attainable
- Relevant
- Time-bound
What are the different types of nursing care plans?
The different types of nursing care plans are:
- Formal care plans (standardised and individualised)
- Informal care plans
- Student care plans



 UK Cities
UK Cities